Residual Networks (ResNets) are a critical building block for training very deep neural networks. They are especially valuable because they help solve the vanishing gradient problem, which traditionally made it difficult to train deep models effectively.
You can learn more about the vanishing gradient problem here.
How Do Residual Networks Solve the Vanishing Gradient Problem?
In a residual network, we pass the input \(x\) directly to a deeper layer through a skip connection. This means that even if the weights in the deeper layers (inside the residual block) become very small during training, they won’t completely block the flow of useful information. As a result, the earlier (shallower) layers can still learn effectively, and the model becomes significantly more stable during training.
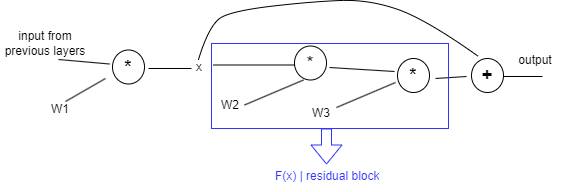
Image by the author
Intuition Behind the Residual Block
Let’s denote the residual function as \(F(x)\), which represents the stacked layers in the residual block. The final output becomes:
\[\text{Output} = F(x) + x\]- If \(F(x)\) learns meaningful patterns, that’s ideal.
- But if \(F(x) \approx 0\) (e.g., the residual block fails to learn), no problem — the skip connection ensures that the input $x$ still flows forward, preserving the network’s ability to learn.
This mechanism ensures that even if the deeper layers don’t contribute much (or at all), the gradient can still flow back through the identity connection.
Gradient Flow Through Residual Connection
Thanks to the skip connection, the gradient with respect to $x$ is:
\[\frac{\partial L}{\partial x} = \frac{\partial L}{\partial \text{output}} + \left(\frac{\partial L}{\partial \text{output}}\right) \cdot W_2 \cdot W_3\]This shows that:
- The first term allows the gradient to bypass the residual block completely.
- The second term allows it to flow through the block.
Together, these terms help mitigate the vanishing gradient issue and make training deep networks feasible.
If W2 and W3 are large, they contribute more significantly to the gradient flow — and therefore, they play a bigger role in updating the weights during backpropagation. This makes it possible for the residual block to effectively learn deeper representations when needed.